Methods to Gain Reliable and Accurate Geospatial Data in Tm Malaysia Map
28 January 2022
Geospatial data may be used by businesses to enhance and preserve their target market. Customers’ preferences can be discovered from the data and help businesses figure out how well their business will do in a specific location. Customers in different locations may have various interests in your products and services. Hence, you may open a business in a location where most people are interested in what you offer.
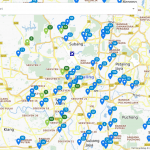
Continuous map updating is our top priority at TM with a constant schedule and method to ensure data quality and accuracy. As a result, our customers may feel more confident when planning, marketing, and managing their businesses with SmartMap.
The data sources gathered are divided into three categories: gathered content, map feedback, and surveys.
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Related Posts
Find nearest mosque to you by using TM ONE SmartMap Malaysia map.
TM ONE SmartMap API as the geocoder to batch geocode and visualize in QGIS the data results.
Geographic Information System (GIS) is software used to view, edit and analyze all types of geograph...